Fill form to unlock content
Error - something went wrong!
Stay up to date with the latest IoT and network edge news.
Subscribed.
Medical Imaging Enhanced by AR and AI Advancements

With all the advances in modern medicine, it’s hard to imagine how different the diagnostic scene was before Wilhelm Roentgen accidentally discovered X-rays in 1895. Finding a tumor or broken bone was limited to physical examination and the doctor’s best guess. Within the first year of the discovery, doctors in Europe and the U.S. were using X-rays to locate bullets from gunshots, bone fractures, kidney stones, and swallowed objects. By 1900, the X-ray was essential for clinical care.
Today, imaging—from X-ray to MRI—touches just about every facet of patient care, diagnosis, and treatment. And the latest health tech applications in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Augmented Reality (AR) are bringing a disruptive new dimension to advanced medical imaging, with the potential to be just as revolutionary as the original discovery of X-rays.
One company on the front lines of this revolution is Novarad, a provider of healthcare solutions. From groundbreaking imaging to real-time analytics at the edge to secure data sharing, Novarad uses responsible AI to improve patient care and healthcare
Augmented Reality Enhances Surgical Planning
Novarad’s OpenSight AR surgery system renders 2D, 3D, and 4D digital images from any modality into a highly detailed hologram. This allows clinicians to look at patients and essentially see through them at the same time—giving doctors the ability to see interactive 3D imaging studies. Radiologists, physicians, and surgeons can use Microsoft HoloLens AR goggles to both interact with the imaging data and see the images displayed, anatomically correct, on the patient.
“This advancement in imaging takes some of the guesswork out of medicine, lowers the risk to the patient, and allows the surgery to be more precise,” says Wendell A. Gibby, M.D., CEO of Novarad. “And it’s much cheaper than the traditional methodology, which has been to take a 3D image and load it into a surgical guidance system that's five times as expensive.” (Figure 1)
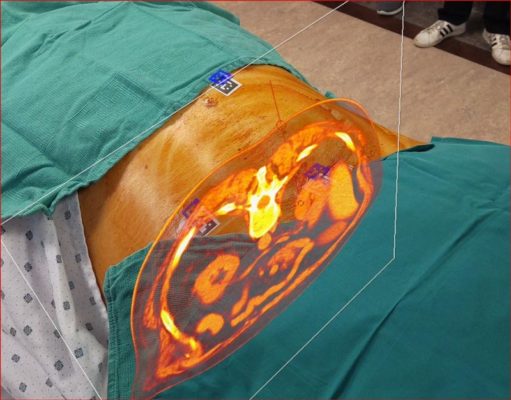
“I had a patient who was in a lot of pain from a very degenerated back,” says Gibby. “We attempted to do an epidural steroid injection, but the thoracic spine was so tight, we couldn't find an entry point. Using a CAT scan and aligning the AR guidance system, we were able to find one little hole that we could get through. It gave me my optimal entrance point, angle, and depth—and ultimately a successful completion of the procedure.”
With @novaradcorp, the latest health tech applications in AI and AR are bringing a disruptive new dimension to advanced imaging.
Creating Actionable Data from Vast Stores of Medical Imaging
Since imaging is central to medical diagnosis and treatment, it makes sense that clinicians want access to as much data as possible to make medical decisions. And although there are vast stores of data, too often that data is underutilized because it’s difficult to access it in a meaningful way.
“Novarad has provided the connection between this large, massive amount of data that comes into a radiology department, and the ability to process it to create intelligible and actionable data that can be distributed to doctors for advanced processing,” says Gibby.
While many medical images can be stored in the cloud, the exciting future of digital imaging using 3D and 4D techniques requires analyzing data to be at the edge for quick viewing.
That's why Novarad created an EdgePACS solution to bring AI capabilities to local workstations, using powerful hardware. Extracting information about the tumor that can't be seen, evaluating the risk of diabetes in someone with increased abdominal adipose tissue, or teasing out brain function in a traumatic injury—all that requires real-time analytics. And radiologists don’t have time to wait for the cloud.
“Edge compute gives us the ability to handle massive amounts of data at the local level, and Intel® is helping with the computer technology to make that possible,” says Gibby.
Making Medical Imaging Readily Accessible—and Secure
While being able to easily transfer patient data in a clinical care ecosystem is convenient and a great time saver, healthcare organizations need to consider and accommodate HIPAA compliance and security concerns. Novarad solves this challenge with CryptoChart, a secure solution to share medical images .
CryptoChart generates a simple QR code that enables recipients to access, view, and share images from their mobile device or desktop. “We take the password, login, website, and identifying information and embed that into an optical code. Literally, it's a 300+ character, or over 3,000-bit, encrypted password,” Gibby explains. “The beauty of it is, if someone somehow manages to crack that, they only get one study because it's tied to each individual.”
The Past Predicts the AI Advancements of the Present
One of the first images Wilhelm Roentgen made was of his wife’s hand, which showed her fingers and the ring she wore. When she saw the image, Mrs. Roentgen supposedly said, “I have seen my death.” Today, perhaps she would be pleased to see how much her husband’s discovery—and the technology subsequently built upon it—has improved healthcare outcomes and enhanced the lives of people all over the world.
This article was edited by Christina Cardoza, Associate Editorial Director for insight.tech.
This article was originally published on April 2, 2020.